|
|||||||||||
|
|
Members of the Kingdom Fungi surround us on a largely microscopic scale, they impact our
lives on all levels: health, food, value of property (e.g., mold and wood rot). Currently
there are hundreds of complete fungal genomes available from various genome projects
(i.e., JGI, Broad Institute, SGD, AspGD, etc…). However, this information is not centralized
or easy to use for systematic analysis. To address this situation, we have developed the
"Fungal Genome Collection (FGC)". The FGC provides a central repository for fungal genomes of all genera. Comparative genomics information is available for all genomes by way of blast similarity search results against the NCBI nonredundant database, against the UniProt/Swissprot database, and also between all fungal genomes. Blast results are organized in such a way that searching for proteins unique to specific fungal genomes, those unique to the fungal kingdom, or those shared with metazoans or plants, can be done easily. In order to facilitate more efficient functional annotation of diverse fungal genomes, we are adding additional information for each protein sequence. These include: gene ontology information, cellular localization prediction, secondary structure and transmembrane predictions, protein family/domain. A user can navigate through the FGC website using an intuitive and user-friendly graphic interface following the fungal phylogeny. It provides data-search capability through all genomes and comparative analysis. Sequence data and analysis results can be downloaded in various formats. The basis for the analysis presented in this database is the set of fungal genomes gathered from several public sites. |
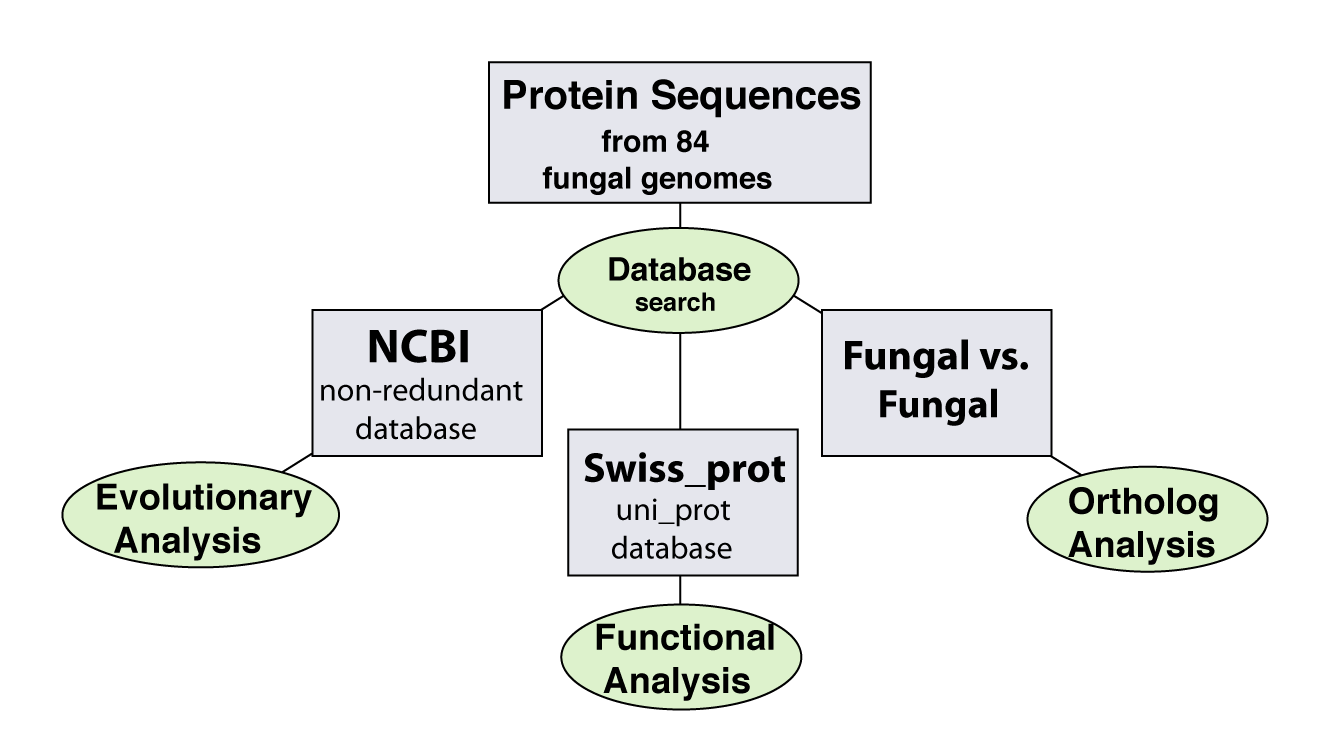
| There are three main areas of analysis avaialbe in FGC. For the evolution analysis, all protein sequences are queries in a blast search against the NCBI non-redundant database. The function analysis is based on BLAST serach against the Swiss_prot database and ortholog candidate analysis is based on a pairwise blast search of each sequence against the seqeunces in all of the other genomes. |
|
|
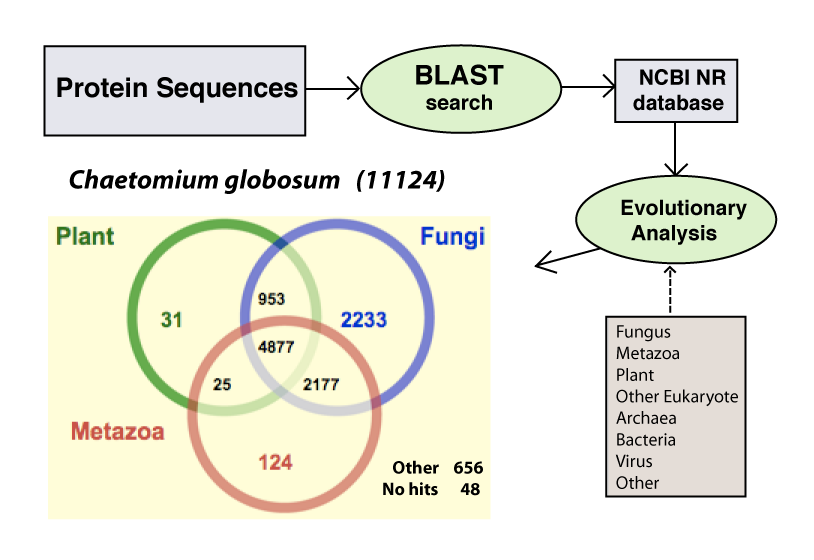
BLAST similarity search results are summarized in three taxonomical groupings (fungal, metazoa, and plants) and shown along the fungal phylogeny. Each fungal species name is linked to the species genome summary page as shown in the inset. BLAST hit numbers are linked to the tables including more detail information |
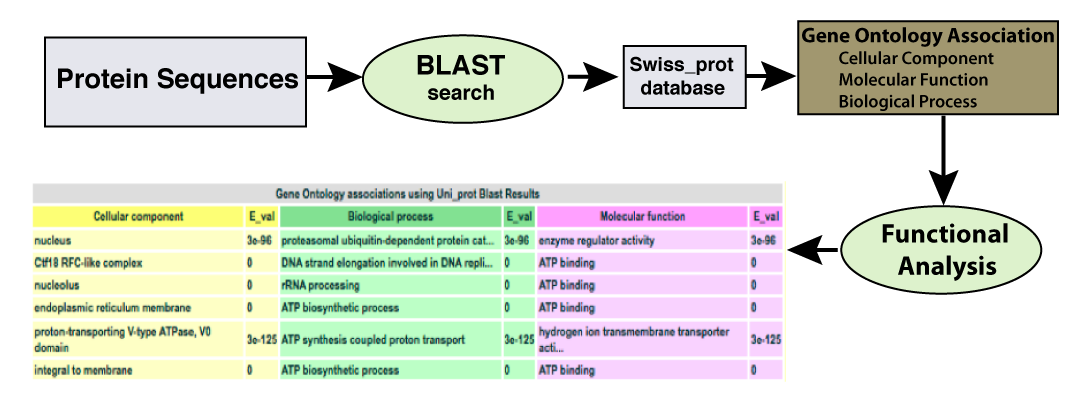
| The GO annotation available from Uniprot is gathered from the results of a BLAST search of each protein sequence against the swiss_prot database. Determining the function of an unannotated protein can be assisted by reviewing these results at increasing percent idenity. |
|
|
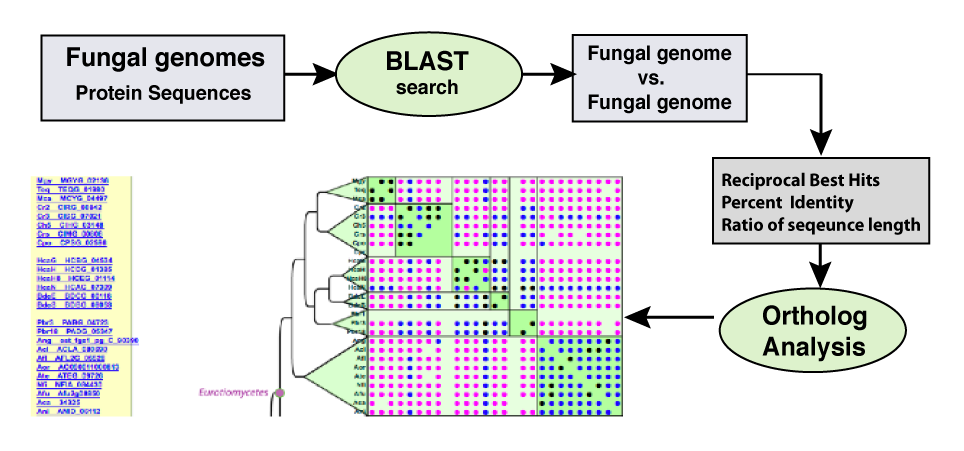
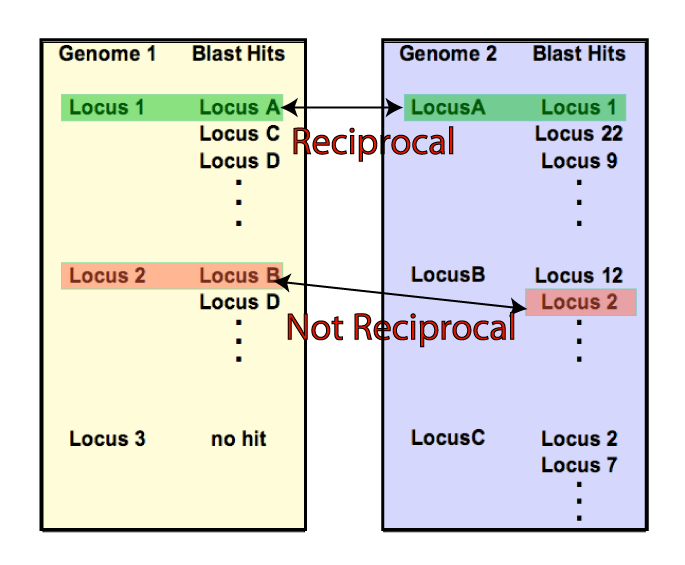
The display of the ortholog candidates between all species for a specific protein (locus) as determined by reciprocal best hit. |
| A reciprocal best hit (left) is a pair of proteins, one from each species that are each others best hit from a BLAST search. A venn diagram (above) displaying the number of reciprocal best hits shared between up to 4 species can be generated using a percent identity selected from a range of 30 -100% identity as selected by the user. This allows ortholog candidates to be determined based on evolutionary distance. These ortholog sequences can be downloaded in Fasta format for further analysis. |
|
|
| NFS grant: DBI - 0743783 |